Summary: Factoring is a form of financing that helps companies with cash flow problems due to slow-paying clients. It allows your business to finance invoices, which improves your company’s working capital.
Factoring transactions are structured as the sale of accounts receivables rather than as a business loan. Consequently, they can be set up quickly and are easier to obtain than conventional loans. Small and midsize companies typically use this solution to improve their cash flow.
This article is a comprehensive tutorial about factoring in Canada. We cover the following subjects:
- Are you giving 30- to 60-day terms to clients?
- How does invoice factoring work?
- Advance rates are important
- Typical factoring rates
- Does your company qualify?
- Benefits of factoring
- Types of invoice factoring
- Industry-specific alternatives
- How to choose a factoring company
- The factoring application process
1. Are you giving 30- to 60-day terms to your clients?
Do you have clients that take 30, 50, or 60 days to pay invoices? In today’s environment, most commercial sales involve payment terms. Terms can give your customers up to two months to pay an invoice.
Offering terms can create cash flow problems because many small and midsize companies can’t afford to wait that long for a payment. They need money to pay for current expenses – like staff salaries and vendors.
The solution: Factor your invoices
Invoice factoring solves this problem. It provides you with an advance on your invoices from slow-paying commercial clients. You get immediate working capital that you can use to pay for important expenses.
2. How does invoice factoring work?
Most factoring companies structure their transactions as the sale of an asset. Basically, you are selling the financial rights to your invoices in exchange for an immediate payment.
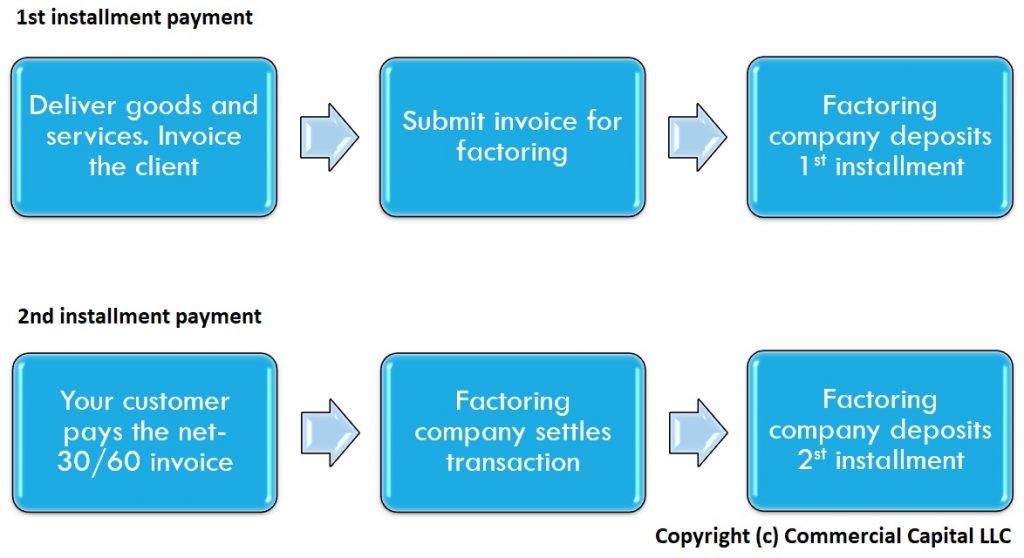
Factors buy your invoices in two installments – the advance and the rebate. The advance covers up to 80% of the invoice and is deposited to your bank account immediately. Note that the advance varies by industry and by company.
Once your customer pays, the factor rebates the second installment to cover the remaining 20%, less any fees. This payment settles the transaction for that specific invoice.
Most transactions follow these steps:
- Your company delivers the goods/services to your client.
- You submit an invoice for financing
- The factoring company advances 80% of the invoice (this amount varies)
- Your client pays after 30 to 90 days
- The factoring company issues a rebate of 20%, less the finance fee.
Go deeper: Learn more about how factoring works.
3. Advance rates are important
Most clients focus on getting the lowest possible rate. However, the combination of factoring rate and advance determines the true cost of factoring. The advance rate varies based on your industry and perceived risk. Here are some average advances. Note that each factoring company uses its own criteria:
| Industry | Advance Rate |
|---|---|
| General Business | 70% – 85% |
| Staffing | 90% – 92% |
| Transportation | 90% – 96% |
| Construction | 70% – 80% |
4. Typical factoring rates
The cost of factoring invoices varies based on the creditworthiness of your clients, the number of invoices you have, the size of the invoices, and the factored volume.
Typical rates average from 1.15% to 4.5% per 30 days. However, rates can be broken down into shorter or longer increments, as required by the transaction. Also, rates vary by industry and other criteria.
5. Does my company qualify?
Factoring has easier qualification requirements than most types of financing, such as loans or lines of credit. The two most important requirements are that your invoices:
- Must be due from reputable commercial/government clients
- Must not have any liens or encumbrances
Also, your company should not have major tax and legal issues, and management should have industry experience. By the way, factoring can be used by companies with tax issues as long as there is a tax payment plan in place.
Go deeper: More details about invoice factoring requirements.
6. Benefits of factoring
Factoring has a number of advantages over other types of small business financing. The obvious benefit is that it can improve your cash flow.
However, there are other benefits. Invoice factoring is available to small businesses and can be deployed quickly. Additionally, the financing line is indexed to your company’s sales, so it can grow alongside your revenues.
Consequently, factoring can be a great alternative form of financing for entrepreneurial companies that are growing quickly but are running into cash flow issues.
7. Types of invoice factoring
There are two types of factoring products: full recourse and non-recourse solutions. Unfortunately, there is a lot of confusion among clients regarding these two options.
Full recourse factoring: In a full recourse plan, the factor has the option to sell an invoice back to you if it’s not paid after 90 days.
Non-recourse factoring: In a non-recourse plan, the factor cannot sell the invoice back to you if it’s not paid after 90 days, as long as the reason for non-payment is a credit problem. This last point often causes confusion. Many factoring companies define a credit problem as a declared bankruptcy. However, this definition varies by factor.
The better plan is actually a matter of personal choice. In the past, there were substantial differences in pricing between plans. This is no longer the case. Also, recourse plans can be a bit more flexible than non-recourse plans.
8. Industry-specific alternatives
Most companies that use factoring benefit from using the general version of invoice factoring. However, factoring companies have also developed some solutions that are customized for specific industries, including:
9. How to select a factoring company?
Choosing the right factoring company is a critical decision for your business. This decision should be made carefully. The following six points provide some guidelines for the process:
a) Avoid overwhelming yourself
One of the greatest mistakes that potential clients make is submitting an application to every factoring company that they speak to. Submitting too many applications and managing multiple proposals can be confusing and take a lot of time.
Instead, call a number factoring companies until you find two or three that meet your criteria. Then, submit an application to only those factors. This approach is more effective and provides you with more competitive factoring proposals.
b) Do they wok in you province?
Some factoring companies can work in every Canadian province, while others offer services only in some provinces. Additionally, only a few factoring companies offer services in Québec due to differences in the legal systems (e.g., PPSA vs Hypothèques).
c) Is their proposal competitive?
The factoring market is competitive, which is good for clients. Consider getting quotes from at least two or three companies. Then compare the quotes to determine which one offers the best value.
Note that price/rate is not the only thing you should be looking at. Review the proposals as a whole and compare them point by point.
d) How long have they been in business?
The first question to ask a factor is how long have they been in business. In this industry, longevity matters. You want to work with a company that knows how to manage a factoring portfolio and can weather economic downturns.
Work with a company that has been operating for at least five years. Longer is better, obviously. It’s OK to work with a company that has been in business for less time. However, verify that it is owned and managed by experienced industry professionals.
e) Do they work with companies in your industry?
Although most factoring companies portray themselves as generalists, most have a few industries that they specialize in. Your company is best served if you work with a factor that knows the details of your industry well. There is a simple way to find out this information – ask the factor directly.
f) Do they work with companies of your size?
Most factoring companies advertise that they can fund companies of any size, from $10,000 to five million dollars. While they may have the funds to pursue these opportunities, they don’t always have the expertise.
The fact is that most factoring companies have a preferred range, such as from $50,000 to $700,000. Only a few companies can actually handle a wide range of opportunities. As with the previous question, it’s best to ask the factor directly.
g) Do they have minimums?
Some factoring companies add minimum factoring volumes to their contracts. It means that your company is contractually required to factor a minimum value while the contract is in place. There is a financial penalty if you factor less than the minimum. The penalty usually covers the difference in fees between what you actually factored and the contractual minimum.
Contrary to advertisements, minimums are not necessarily bad. Most factors provide you with a lower factoring rate if you agree to certain minimums. As long as you are certain you will not break the minimums, they can get you lower prices.
Keep in mind that breaking a factoring minimum is usually bad and affects your profits. If your plan has minimums, negotiate them carefully.
10. The factoring application process
Applying for a factoring program is much easier than applying for a commercial line of credit. As long as you have all the needed documents, the process usually takes a couple of days. Most factoring companies ask for:
- An application
- Articles of incorporation or LLC operating agreement
- Recent receivables aging report
Aside from asking for these three items, each factoring company is different. Some may ask for other reports, while others won’t.
Want an instant quote?
Looking for factoring companies? We can provide you with high advances and rates as low as 1.15%. Get an instant quote or call (877) 300 3258 to speak with an expert.





